Hair loss can be a distressing experience for both men and women. Whether it’s gradual thinning or more sudden shedding, many of us have stood in front of the mirror and wondered, “Is there anything that actually works?” One name that’s been gaining more and more attention in recent years is oral minoxidil.
You might be familiar with topical minoxidil, the over-the-counter solution or foam found in most drugstores. But now, dermatologists and hair specialists are increasingly turning to its oral form as a powerful alternative for managing various types of hair loss.
Let’s take a deep dive into what oral minoxidil is, how it works, what the science says, and whether it might be a good option for you.
What Is Oral Minoxidil?
Minoxidil was originally developed in the 1970s as a medication for high blood pressure. During those early days, doctors noticed something unusual: patients taking minoxidil were growing hair—a lot of it. This unexpected side effect paved the way for the development of topical minoxidil, which has been FDA-approved for hair loss since the 1980s.
But what about the pill form?
Oral minoxidil uses the same active ingredient, just delivered in a low-dose tablet instead of being applied directly to the scalp. Initially overlooked due to concerns about side effects from the higher blood pressure doses, oral minoxidil is now being prescribed in micro-doses for hair regrowth with encouraging results.
Who Is It For?
Oral minoxidil isn’t just for people with male pattern baldness. It’s being used to treat a wide range of hair loss conditions, including:
- Androgenetic alopecia (male and female pattern hair loss)
- Chronic telogen effluvium (persistent shedding)
- Alopecia areata
- Traction alopecia
- Scarring alopecias
- Hair loss after chemotherapy
- Eyebrow and beard regrowth
If you’ve tried topical treatments without success or experienced scalp irritation, oral minoxidil may be a more convenient and effective alternative.
How Does Oral Minoxidil Work for Hair Loss?
While the exact mechanisms of oral minoxidil aren’t fully understood, research and clinical experience point to several key ways it promotes hair growth:
- 🩸 Vasodilation: It widens blood vessels, improving blood flow and oxygen supply to the hair follicles.
- 🔄 Anagen Phase Extension: It prolongs the growth (anagen) phase of the hair cycle.
- 🔥 Anti-inflammatory Effects: It helps reduce inflammation, which is especially helpful in conditions like scarring alopecia.
- 🧬 Stimulation of Growth Factors: It may promote the release of factors that support follicle regeneration.
- 🔒 Mild Anti-androgenic Activity: Some studies suggest oral minoxidil might reduce the activity of DHT, the hormone involved in pattern baldness.
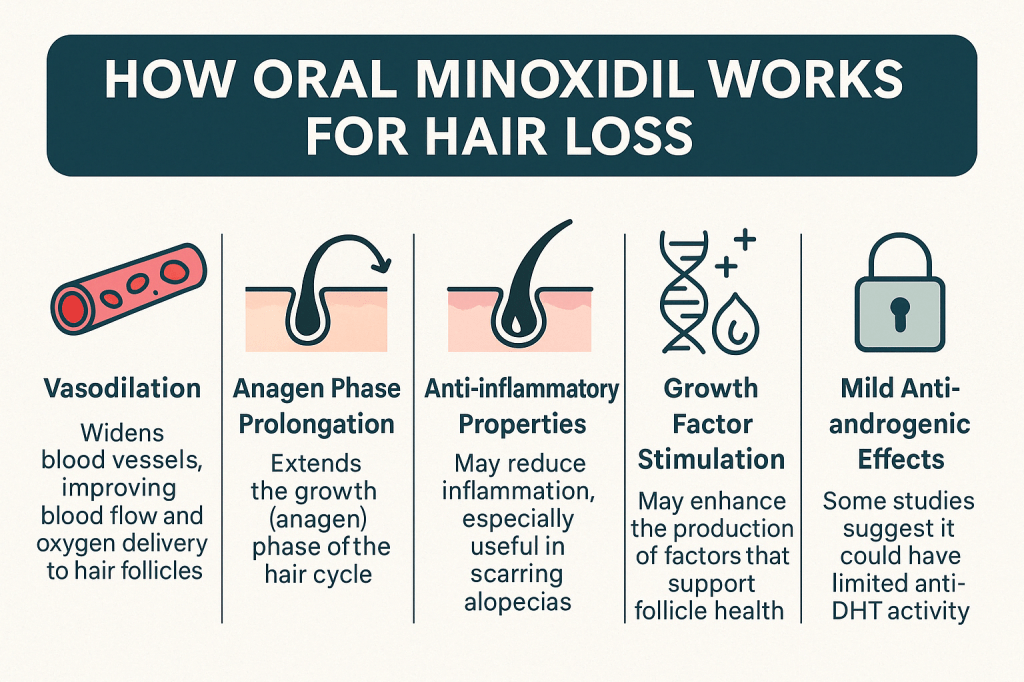
These combined effects make oral minoxidil a multi-faceted approach to hair restoration, helping both retain existing hair and promote new growth.
What Results Can You Expect?
Patience is key.
Most people start seeing noticeable results between 3 and 6 months after beginning treatment, although some may see early signs like reduced shedding within the first few weeks. Hair regrowth takes time, and the full benefits of oral minoxidil often become clearer after 6 to 12 months of consistent use.
Results may vary depending on factors like age, the extent of hair loss, and how early treatment begins.
Also important: The effects are not permanent. If you stop taking oral minoxidil, the gains will gradually diminish over several months. Like brushing your teeth, it’s a routine you have to stick with if you want to maintain the benefits.
Dosing: How Much Is Enough?
For treating high blood pressure, oral minoxidil is typically prescribed in doses ranging from 10 to 40 mg per day. For hair loss, the dosing is much lower:
- Women: 0.25 mg to 1.25 mg per day
- Men: 1 mg to 5 mg per day
Some dermatologists start patients on the lower end and adjust based on results and side effects. It can be taken with or without food, and often at bedtime to help minimize side effects like lightheadedness.
Why Choose Oral Over Topical?
There are several advantages to choosing oral minoxidil over the topical formulation:
- 🌿 Better Hair Regrowth: Oral minoxidil has shown stronger regrowth results in some studies.
- ⏰ Once-Daily Dosing: No need to apply it twice a day like the topical version.
- ✅ No Scalp Irritation: People who get itchy, flaky skin from the topical formulation often do better with oral.
- 🎁 More Affordable: Surprisingly, oral minoxidil is often cheaper than topical treatments.
- 🤠 No Styling Issues: No greasy residue, no foam or liquid to interfere with your hair routine.
What Are the Side Effects?
Most people tolerate oral minoxidil well at low doses. Still, as with any medication, side effects can occur. These fall into two categories: mild and serious.
Mild Side Effects:
- 👁🗨 Hypertrichosis (unwanted hair growth, especially on the face)
- 😕 Headaches
- 😬 Dizziness or lightheadedness
- 🩸 Mild leg swelling
- ❤️ Increased heart rate
For many, these effects can be minimized by adjusting the dose or taking the pill at night.
Rare but Serious Side Effects:
- ☕️ Fluid retention
- ❤️ Pericardial effusion (fluid around the heart)
Though extremely rare at low doses, pericardial effusion is the side effect that has sparked the most debate. There have been case reports even at low doses, though causality hasn’t been definitively established. Still, it’s something to be aware of, and anyone with heart conditions or low blood pressure should consult a specialist before starting treatment.
In a large multi-center study involving over 1,400 patients, only about 1% stopped taking oral minoxidil due to side effects.
Debates and Concerns: What Critics Say
Despite the growing popularity, not everyone is ready to jump on the oral minoxidil train.
Skeptics point to the lack of large, long-term prospective studies, and emphasize that most data we have comes from retrospective case reviews or small-scale clinical trials. Concerns include:
- Potential for under-reported serious side effects
- Lack of rigorous cardiac monitoring protocols in some settings
- Risk of promoting self-medication due to social media hype
And then there’s hypertrichosis. While some patients are happy to see thicker eyebrows or facial hair, others find it a nuisance. Women in particular may find this side effect distressing.
These are valid concerns, and they highlight the importance of working with a qualified healthcare provider who understands both the science and the art of treating hair loss.
How to Get It
Oral minoxidil is prescription-only in most countries, including the United States. You won’t find it next to the shampoo aisle.
Not all doctors feel comfortable prescribing it, especially outside of dermatology. If you’re interested in trying oral minoxidil, your best bet is to speak with a hair loss specialist or dermatologist who stays current with the latest research and treatment options.
Final Thoughts: Is Oral Minoxidil Right for You?
Oral minoxidil represents an exciting shift in how we approach hair loss treatment. It’s not magic, and it’s not without risks, but for many patients it offers real hope where other treatments have failed or caused irritation.
If you’re struggling with hair loss and considering your options, oral minoxidil might be worth discussing with your doctor. Just make sure you get the facts, set realistic expectations, and stay consistent.
Hair regrowth takes time, but with the right plan in place, you may find that the mirror starts to reflect something you’d almost forgotten: your confidence.
Disclaimer:
This article is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a licensed healthcare provider before beginning any new medication or treatment for hair loss, including oral minoxidil. Results may vary, and all medications carry the potential for side effects.